What is MP4? Here's Everything You Need to Know
In today's digital age, videos dominate our online experiences. From streaming platforms to social media feeds, videos are everywhere. But have you ever wondered what makes these videos accessible across various devices and platforms? Use MP4, the unsung hero of multimedia file formats. Here, we'll get into the world of MP4, exploring its origins, structure, advantages, and how it compares to other formats. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of what is MP4 and why it's essential in our digital lives.

Part 1: What Is MP4?
MP4, short for MPEG-4 Part 14, is not just a file extension; it's a revolutionary container format that revolutionized the way we store and share multimedia content. Unlike traditional formats that focus solely on video or audio, MP4 is a versatile container that can hold various types of data, including video, audio, images, and subtitles. Think of it as a digital Swiss Army knife, capable of encapsulating all the elements necessary for a seamless multimedia experience.
Part 2. Brief History of MP4
The story of MP4 dates back to the 2000s when the Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) set out to create a standardized format for streaming multimedia content over the internet. The first version of MP4 was based on the QuickTime format specification and was published as a revision of MPEG-4 Part 1: Systems. Over the years, MP4 has undergone several revisions, with the latest being ISO/IEC 14496-14. Today, it serves as the foundation for many popular file formats, including 3GP.
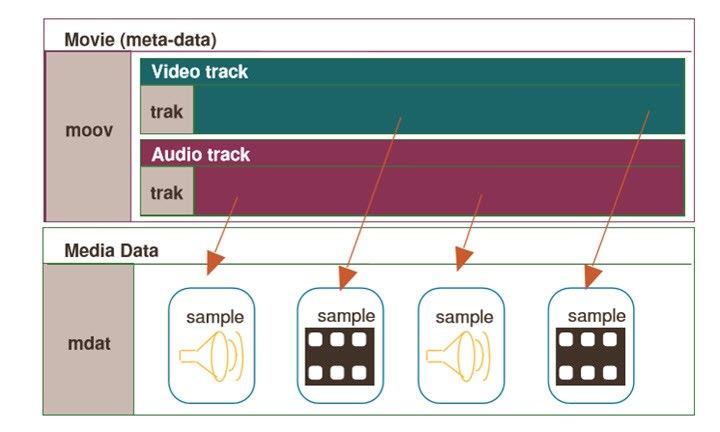
Part 3. MP4 File Structure
At the core of MP4 lies its unique file structure, which is divided into two main segments: media data and metadata. Media data encompasses streams of video, audio, and subtitles, while metadata provides essential information about the file, such as timestamps and random access points. This structured approach ensures that MP4 files are not only compact but also easily accessible across different platforms and devices.
Part 4. Advantages and Disadvantages
In an era marked by the coexistence of numerous file formats, MP4 stands out as a frontrunner due to its remarkable compatibility across various platforms. It enjoys widespread native support on TVs, mobile phones, computers, multimedia software, and web browsers. However, like any format, MP4 boasts both commendable features and certain drawbacks.
Advantages of MP4 File
- Versatility: MP4 is well-suited for tasks such as HTTP streaming, broadcasting, and editing.
- Minimal Quality Loss: Through collaboration with efficient codecs, MP4 facilitates reduced quality loss and smaller file sizes. Its ongoing development promises further enhancements alongside future compression methods.
- Flexible Modification: MP4's structure allows for independent storage of each data component, enabling users to extract audio, subtitles, or perform tasks like remuxing MKV to MP4.
- Extensible Application: Support for metadata empowers MP4 files with additional user interaction features such as navigation options, menus, 3D graphics, and VR videos.
Disadvantages of MP4 File
- Resource-Intensive: Processing MP4 files demands significant computing resources due to the inclusion of various media data and metadata within a single file.
- Error-Prone: The expansive data capacity of MP4 increases the likelihood of potential errors, including file corruption, incompatible codecs, invalid audio tracks, and audio/video synchronization issues.
Part 5. Compare MP4 and Other Formats
To truly understand the value of MP4, it's essential to compare it to other popular formats like MOV, MKV, AVI, and MP3.

MP4 vs MOV:
MP4 and MOV are two video container formats that share many similarities but were developed by different organizations. MOV is proprietary to Apple and predates MP4, which was standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Initially, MP4 enjoyed broader native support across devices, programs, and video platforms. However, both formats are now widely utilized. Consequently, users may simply convert MOV to MP4 or vice versa, adhering to the recommended settings of the target platform or end device.
MP4 vs MKV:
MKV is a royalty-free video container format known for its support of unlimited media tracks, often utilized for storing HD movies from Blu-ray discs and DVDs. In contrast, MP4 is patent-protected and imposes specific media content limits. While MKV theoretically permits free usage, MP4 remains more popular. Consequently, converting MKV to MP4 may be necessary for platforms like YouTube.
MP4 vs AVI:
MP4 supports a variety of media codecs, particularly those within the MPEG lineup. On the other hand, AVI typically employs Xvid or DivX for video encoding, resulting in high-definition videos but larger file sizes. While AVI enjoys strong support from Microsoft and Android devices, it lacks compatibility with Apple devices and certain social media platforms like Twitter and TikTok. Converting AVI to MP4 with minimal quality loss is often preferred for easier handling of legacy AVI videos.
MP4 vs MP3:
MP3 and MP4 serve distinct purposes in storing media files. MP3 is exclusively used for audio, whereas MP4 can contain audio, video, images, and subtitles. Technically, MP3 represents an audio coding format dictating audio file compression, whereas MP4 functions as a video container format unrelated to coding schemes. MP4 encapsulates multimedia files, including compressed MP3 audio, within its structure.
Part 6. Devices That Support MP4
One of the key reasons behind MP4's popularity is its widespread support across various devices and platforms. From smartphones and tablets to smart TVs and game consoles, MP4 is the format of choice for millions of users worldwide. Whether you're an Apple enthusiast or an Android aficionado, chances are your device can play MP4 files without any hassle. With the help of tools like HitPaw Univd (HitPaw Video Converter), you can easily convert MP4 files to any other format, ensuring compatibility across all your devices.
Part 7. How to Open an MP4 File
Opening an MP4 file is as simple as double-clicking on it or tapping it on your device. Most modern media players, including VLC Media Player and QuickTime Player, support MP4 out of the box. However, if you encounter any issues, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take, such as converting the file to a different format or installing additional codecs.
Part 8: How to Convert an MP4 Video File?
Can I convert MP4 without losing quality? Yes, with a high-quality converter. HitPaw Univd stands out as a versatile and user-friendly tool that empowers users to access any video format they desire.
Main Features
- Convert MP4 to any other formats
- Convert MP4 to different devices and platforms with preset parameters
- Batch convert MP4 files
- Convert 4K/8K videos without losing quality
- Built-in editor enables users to polish videos
- 120x faster conversion speed
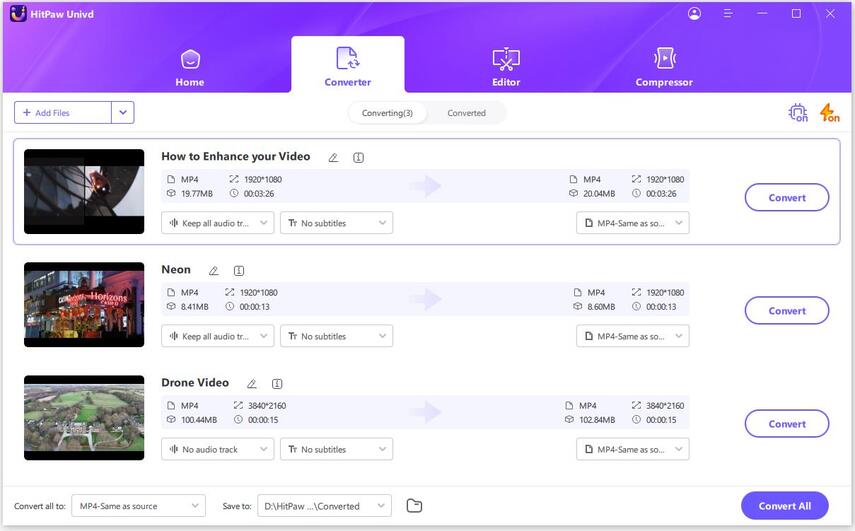
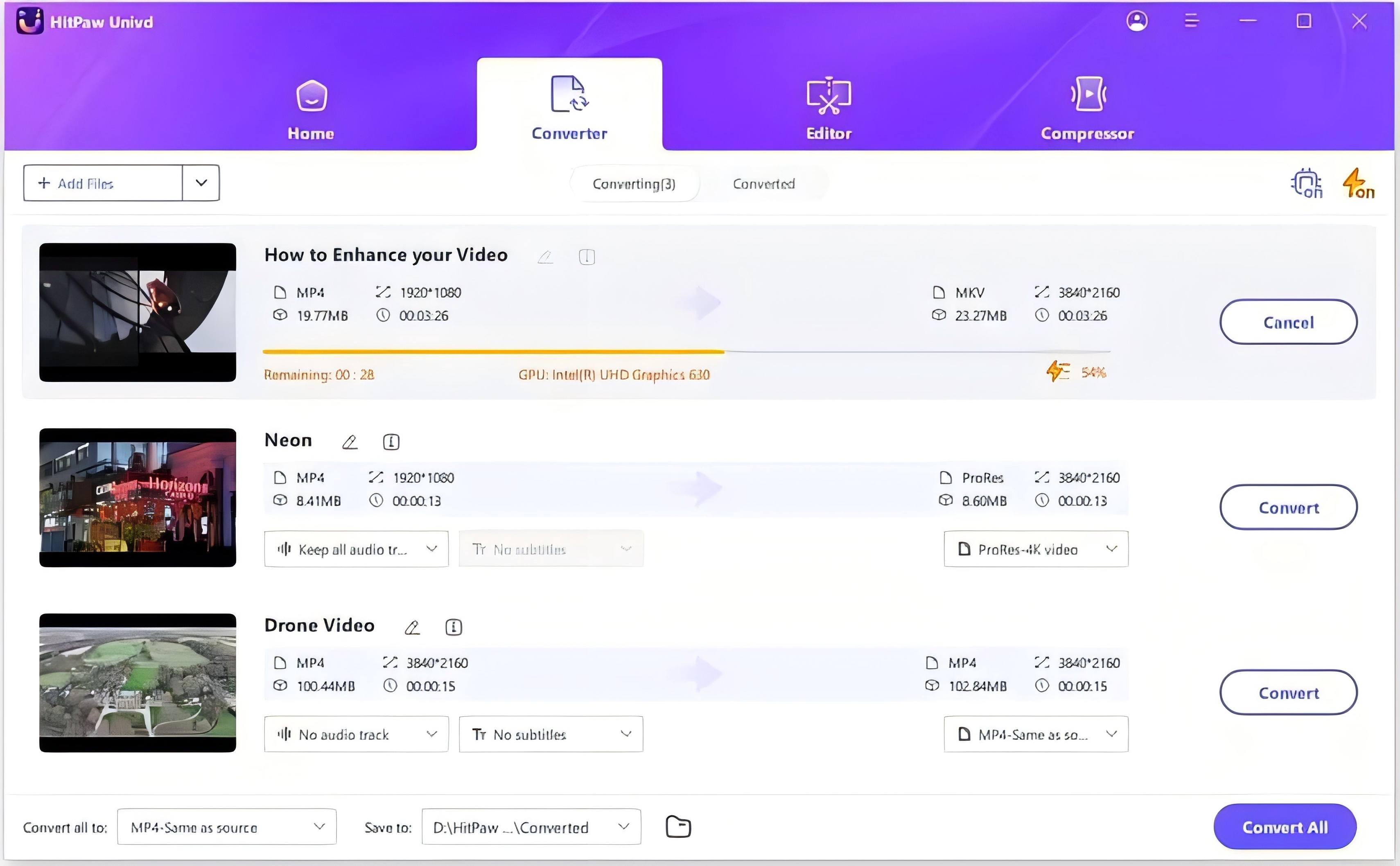
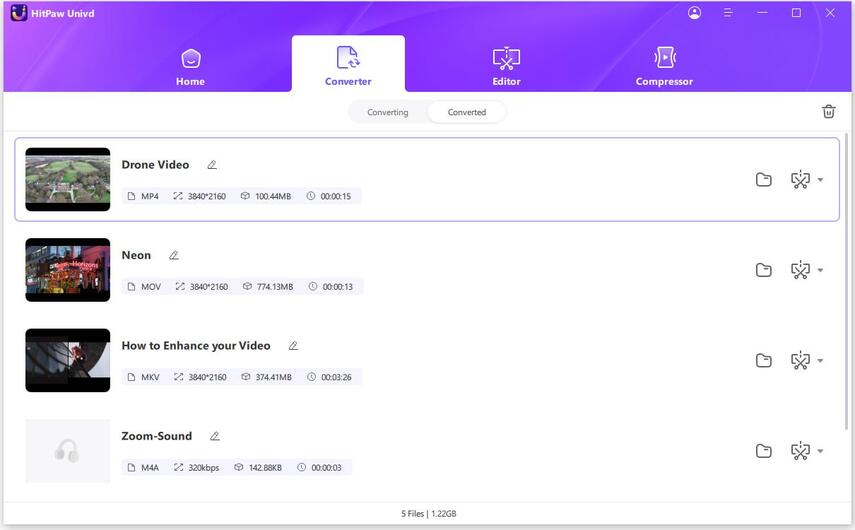
How to Batch Convert MP4 Files
Step 1:Launch HitPaw Univd and import your MP4 files.

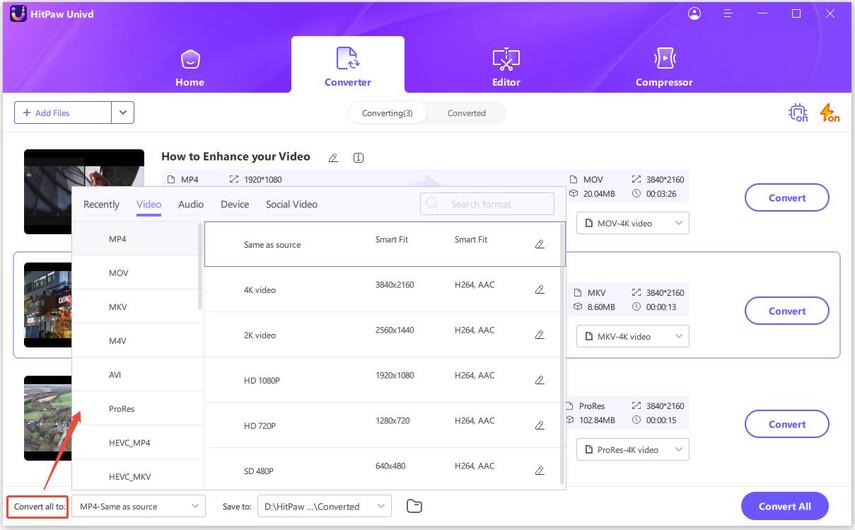
Step 2:Select an output format from the format list.

Step 3:Click Convert All to start converting MP4 without losing quality.

Step 4:Access to the converted videos.

The Bottom Line
Understanding What Is MP4 is not just about grasping a file extension; it's a journey into the heart of modern multimedia. We've also discovered how to seamlessly convert videos using the user-friendly HitPaw Univd. By following the steps provided, you can effortlessly import, edit, and convert your video files, ensuring compatibility and maintaining quality.






 HitPaw VikPea
HitPaw VikPea HitPaw Watermark Remover
HitPaw Watermark Remover 


Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
My passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. With years of hands-on experience, I create content that not only informs but inspires our audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles