Raster vs. Vector: Key Differences and How to Choose the Right Format
Digital graphics come in two fundamental types: raster and vector. These formats form the backbone of countless creative and professional projects, from website graphics and logos to detailed photo editing and CNC machining. Choosing the right format isn't just a matter of preference; it can significantly impact the outcome of your work. Should you go with the pixel-rich detail of raster images or the scalability and precision of vector graphics? In this article, we'll break down the difference between raster and vector files, weigh their pros and cons, and guide you on choosing the right format for your needs.
Part 1: Raster vs Vector Images: What Is the Difference?
Raster images are pixel-based, creating intricate visuals ideal for photographs and detailed artworks. However, they are resolution-dependent, meaning resizing can lead to quality loss. In contrast, vector images rely on mathematical formulas to define shapes, making them scalable without sacrificing quality. This makes vectors perfect for logos, text, and geometric designs.
Feature
Raster Graphics
Vector Graphics
Resolution
Resolution-dependent, may lose quality
Scalable without quality loss
File Size
Larger due to pixel density
Smaller due to mathematical definitions
Usage
Photography, web graphics, print design
Logos, typography, CAD designs
File Formats
JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, TIFF
SVG, AI, EPS, PDF
Software
Photoshop, GIMP
Illustrator, CorelDRAW
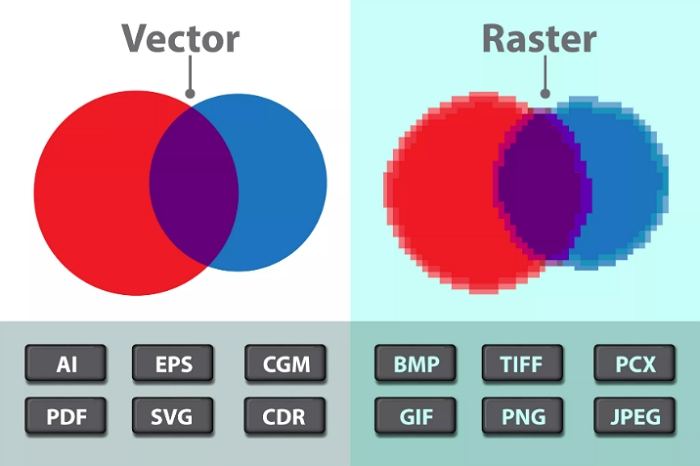
By understanding the difference between a raster and vector image, you can determine the best fit for your creative and professional tasks.
Part 2: Raster vs Vector: Pros and Cons of Raster and Vector Files
When deciding between raster and vector images, it's essential to weigh their pros and cons. Each format has its own set of strengths and limitations that make it more or less suitable for specific uses.
Raster Graphics: Pros and Cons
Raster images excel in creating photorealistic visuals, thanks to their ability to capture intricate details, colors, and shading. This makes them perfect for photography, web design, and print media. However, their pixel-based nature means they aren't scalable without quality loss, and their file sizes can quickly become unwieldy.
Pros
- Handles complex colors, textures, and shading.
- Perfect for hyper-realistic imagery.
- Widely used in photography and print.
- Easily accessible and beginner-friendly.
Cons
- Not scalable; quality reduces on resizing.
- Can result in large file sizes.
- Requires advanced hardware for editing.
- Lower accuracy for certain tasks.
Vector Graphics: Pros and Cons
Vector images are ideal for projects that require scalability and precision. Logos, text designs, and CAD tasks benefit significantly from their ability to remain sharp at any size. However, their limited ability to handle realistic textures and colors means they aren't always suitable for photo editing or web use.
Pros
- Fully scalable without quality loss.
- Smaller file sizes compared to raster.
- Extremely accurate for design and engraving.
- Ideal for CNC machines and CAD tasks.
Cons
- Limited in handling colors and textures.
- Steeper learning curve for beginners.
- Often requires raster elements for complex visuals.
- Less practical for web and photographic use.
Part 3: Raster Graphics vs Vector Graphics: Which Should You Use?
Choosing between raster and vector files depends on your project requirements and how you plan to use the graphics. Each format offers unique advantages that cater to specific tasks.
Common Uses of Raster Graphics:
Best for tasks like photo editing, digital art, and decorative pieces. However, due to resolution dependency, resizing a low-resolution raster image can lead to pixelation.
- Photo engraving
- Personalized items
Common Uses of Vector Graphics:
Perfect for logos, text, and large-scale prints, thanks to their scalability. They are also highly suitable for engraving tasks where precision matters, regardless of object size.
- Marking and branding
- Text and logo engraving
By understanding the difference between raster and vector files, you can select the right format based on your design goals and output requirements.
Part 4: Convert Vector (SVG) to Raster Format (JPG/PNG/WebP/BMP)
Converting raster data to vector format is a crucial process in GIS that enables the transition from continuous, pixel-based data to discrete, geometric shapes. Thanks to HitPaw Univd (HitPaw Video Converter), converting vector images to raster formats has never been easier. This versatile software offers a seamless way to transform your graphics while maintaining the highest quality. Whether you need JPGs for web design, PNGs for transparent backgrounds, or BMPs for print projects, HitPaw simplifies the entire process.
HitPaw Univd - All-in-one Video Solutions for Win & Mac
Secure Verified. 254,145 people have downloaded it.
- Convert images to multiple raster formats (JPG, PNG, WebP, BMP, etc.).
- Batch convert with customizable settings for efficiency.
- Resize, rotate, crop, and compress images with ease.
- Ideal for preparing images for web use, sharing, or mobile display.
Secure Verified. 254,145 people have downloaded it.
Steps to Convert Vector Files to Raster Formats
Step 1:Launch HitPaw Univd and navigate to the Toolbox tab. Select the "Image Converter" option and upload your images.

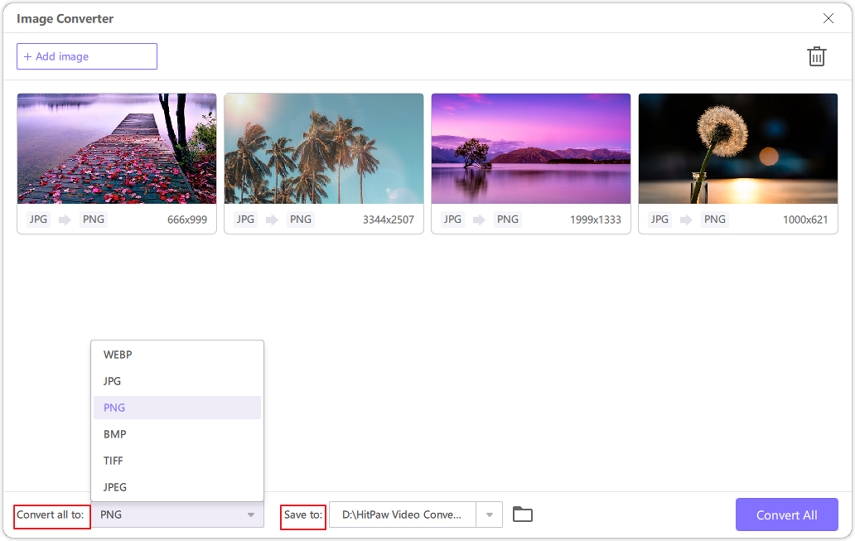
Step 2:Choose the desired raster format (e.g., PNG) as the output. Specify the destination folder for the converted files.

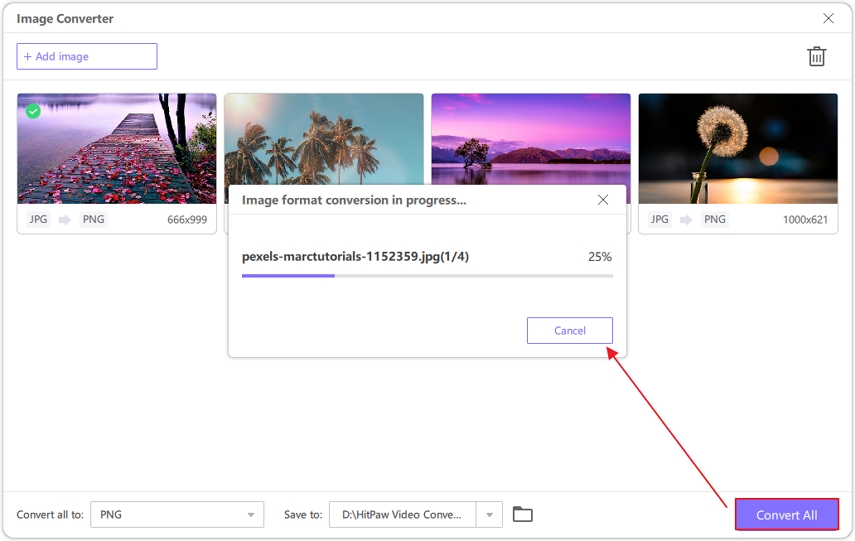
Step 3:Click Convert All to begin the process. HitPaw will swiftly convert your vector files into high-quality raster images.

With HitPaw, converting between raster and vector graphics is straightforward, ensuring you always have the right format for your project.
Part 5: Frequently Asked Questions about Raster vs. Vector Files
Q1. How do you know if an image is a vector?
A1. Check its file format-common vector formats include SVG, AI, and EPS. Vector images remain clear when zoomed in or resized, while raster images lose quality.
Q2. Is Photoshop vector-based?
A2. No, Photoshop is primarily a raster-based software for editing pixel images. It includes some vector tools, but its focus is on raster graphics.
Q3. Is Illustrator raster or vector?
A3. Adobe Illustrator is a vector-based software. It specializes in creating scalable graphics such as logos, icons, and illustrations. Although Illustrator allows raster images to be embedded within projects, its main strength lies in producing resolution-independent designs.
Q4. What is the difference between vector and raster?
A4. Raster graphics are pixel-based and best for detailed images like photos, but they lose quality when resized. Vector graphics are path-based, scalable, and ideal for logos and text.
Q5. Is it better to print vector or raster?
A5. It depends on the project. Vector graphics are better for logos and text, while raster images are best for photos and complex designs. For high-quality prints, raster images should be high resolution (300 DPI).
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between raster and vector images is crucial for achieving the best results in your creative endeavors. Raster graphics offer unmatched detail and realism, while vector graphics excel in scalability and precision. By leveraging tools like HitPaw Univd, you can effortlessly switch between these formats, ensuring your designs meet the demands of any project. Whether you're creating a logo, engraving text, or editing a photo, the right format is just a step away.







 HitPaw VoicePea
HitPaw VoicePea  HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer) HitPaw FotorPea
HitPaw FotorPea



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
My passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. With years of hands-on experience, I create content that not only informs but inspires our audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles