A Comprehensive Guide to Audio File Formats: Pros, Cons, and More
Though some classic listeners prefer their stacks of CDs and shelves of vinyl, others have switched to digital music libraries. These libraries boast music files in digital file formats and are easier to store and access on different devices. If you are into exploring the different formats of audio files and wondering which is the best one to have, we've got you covered! In this ultimate guide, we will dive deeper into the nitty gritty details of 10 common audio file formats, along with their pros and cons. So, without any further ado, let's begin exploring!
Part 1: Uncompressed Audio Format
As evident by the name, uncompressed audio file formats haven't undergone any sort of compression. This means that no data has been lost in compression, and the original recording is preserved in its true form.

1. WAV File Format
Waveform Audio File Format (WAV) is a high-resolution audio file format mainly used for encoding CD audio data. Though these files can store any sort of uncompressed data, they are mostly used for storing uncompressed audio.
Pros
- High quality audio file format
- Diverse compatibility
- Easier to edit
Cons
- Very large file size
- Impractical for everyday use
2. PCM File Format
Music productions mostly prefer Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) because of its premium audio quality. This file format is more like a digital representation of analog signals, and it's the standard audio format used throughout computers and other digital devices.
Pros
- No decoding required
- Uses in CDs, DVDs, and Blu-rays
- The preferred format for music production
Cons
- Not suitable for longer recordings
- Larger file size
3. AIFF File Format
Audio Interchange File Format (AIFF) is quite like WAV. This format is compatible with both Apple and Microsoft systems, but it is seen as rare because of its large file sizes.
Pros
- Metadata support
- Compatibility with Apple devices
- Diverse compatibility with software
Cons
- Limited hardware support
- Large file sizes
Part 2: Lossy Compressed Audio Format
Lossy compressed audio files are created by compressing audio in a way that preserves the main aspects while the unnoticeable audio pieces are sliced away. So, don't expect them to retain 100% audio fidelity. They reduce file size significantly to maximize storage and enable faster online streaming.

1. MP3 File Format
The creation of MP3 audio file format was indeed revolutionary in the early 2000s. It was considered among the most efficient formats for extracting tracks from CDs and storing them on digital hard drives.
Pros
- Basis for early digital audio players
- Low file size
- Wide compatibility and easier to share
Cons
- Lossy audio quality
- Relatively older format
2. OGG File Format
OGG/Vorbis is a term most music enthusiasts are aware of. It refers to an open-source multimedia compression technology mainly used for audio compression. This format is exclusively popular for Spotify streams.
Pros
- Offers better sound quality than MP3 at similar bitrates
- Supports more channels and utilizes VBR compression
- Free and open-source
Cons
- Doesn’t offer metadata support
- Limited compatibility compared to MP3
3. WMA File Format
Windows Media Audio (WMA) is an utterly famed proprietary format developed by Microsoft. It offers slightly improved sound quality than MP3, but it isn't widely compatible with non-Microsoft devices.
Pros
- Efficient audio file format
- Enable easier streaming
- Low file size
Cons
- Limited compatibility
- Lossy compression applied
4. AAC File Format
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is another lossy compressed audio file format that preserves audio track quality better than MP3. It used to be a preferred audio format for iTunes and is still available on varied AAC-compatible devices.
Pros
- Better sound quality than MP3
- Smaller file size
- Multi-channel audio support
Cons
- Doesn’t offer universal support
- More complex to encode
Part 3: Lossless Compressed Audio Format
Lossless audio files are compressed so that the original audio track quality stays intact. This means there won't be any loss of audio pieces during the compression process. The quality of these file formats is close to 16 bits/44.1 kHz or higher.

1. FLAC File Format
Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC) is considered the gold standard of digital audio formats because it has a smaller file size and preserves discernible audio quality.
Pros
- Offers metadata support
- Free to use and modify
- Features high-resolution audio
Cons
- Larger file size than MP3 and AAC
- Requires increased bandwidth
2. WMA File Format
WMA is a widely used audio file format for audio recordings and voice content. It also has a lossless version of WMA Lossless.
Pros
- Improves playback effects
- Enables faster streaming
- Widely supported by Windows devices
Cons
- Deteriorated performance at high frequency
- In great competition with MP3 and AAC
3. ALAC File Format
Developed by Apple, Apple Lossless Audio Codec (ALAC) has diverse uses in the Apple Music catalog.
Pros
- Apple support
- Rips CDs without quality loss
- Recovers damaged original CDs
Cons
- Limited support for non-Apple devices
- Demands robust hardware
Bonus Tip: How to Convert Audio File Format on Windows and Mac?
Third-party platforms, like HitPaw Univd (HitPaw Video Converter), offer seamless audio file format conversions. They offer comprehensive features and support over 1000+ formats. Moreover, conversion preserves audio quality when file size is reduced significantly.
Key Features of HitPaw Univd
- Support for various file formats
- Enables conversion of videos for tablets and phones
- Supports Windows and Mac hardware GPUs
How to Convert File Formats Audio Using HitPaw Univd?
Step 1: Import Audio File(s)Launch HitPaw Univd and hit the Add Audio button on the top left corner. Now, choose Add Audio or simply drag and drop the file you want to convert.
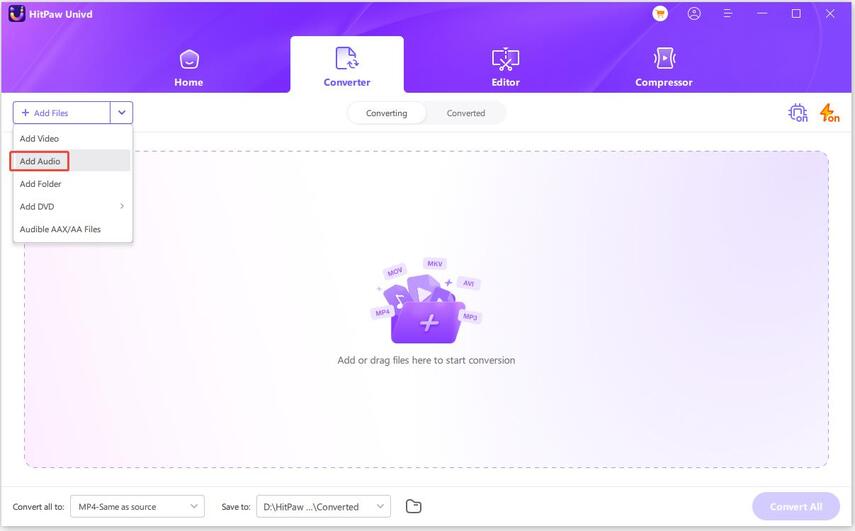
Step 2: Choose Audio Format
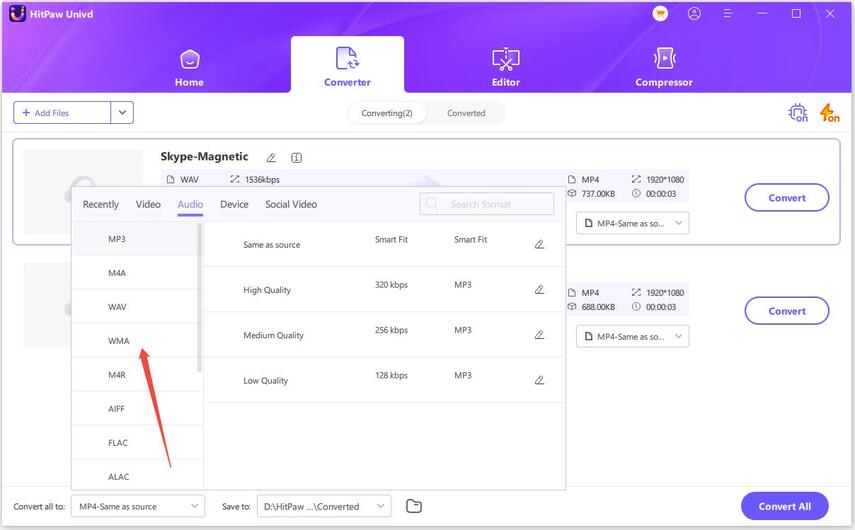
Now, hit the inverted triangle beside the files to choose their output formats. Alternatively, hit Convert All and select a unified output format for all files. In the output format menu, you can switch to the Audio tab to choose quality.
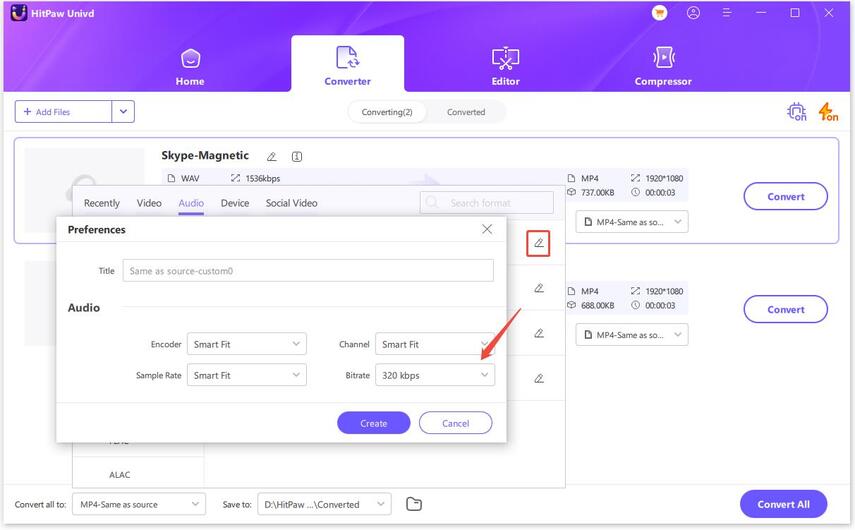
You can also choose to edit the different output formats, like bit rate.
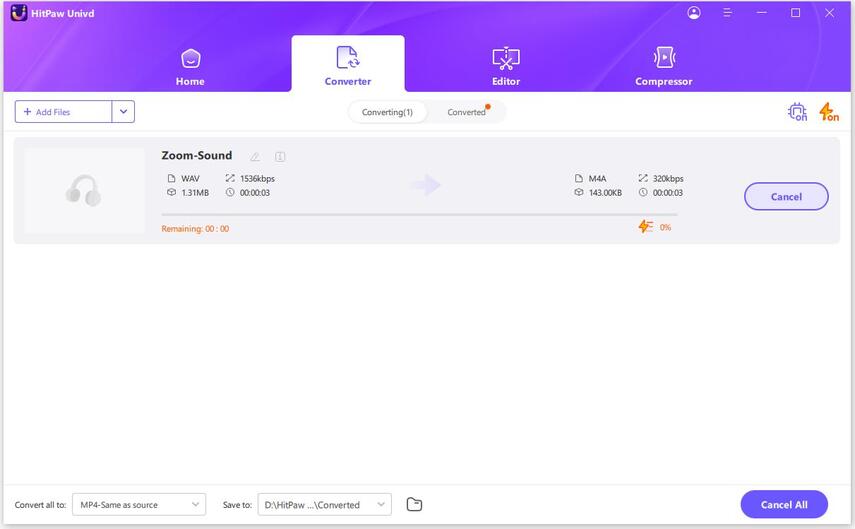
Step 3: Convert Audio
When done with the output settings, click Convert or Convert All to begin lossless conversion.
Step 4: Access the Converted Files
Once the conversion is completed, you can access converted files by converting to the Converted tab.
Conclusion
Audio file formats are diverse – all distributed in three main categories: uncompressed, lossy compressed, and lossless compressed audio file formats. All these have distinct characteristics based mainly on quality preservation and file size. However, if we had to choose the best file format, it would be WAV; still, the most commonly used platform is MP3 for its wide compatibility.
Do you want to convert audio files from one format to another? Check out HitPaw Univd, which supports conversion to and from over 1000 file formats.






 HitPaw Edimakor
HitPaw Edimakor HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer) HitPaw FotorPea
HitPaw FotorPea



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
My passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. With years of hands-on experience, I create content that not only informs but inspires our audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles